Video Bitrate: How to Choose the Ideal Bitrate for Your Video

- What is bitrate: The Full guide
- Video bitrate meaning
- Video bitrate measurements
- How does bitrate affect video quality?
- Bitrate and bandwidth limits
- How to deal with bandwidth limits
- Buffer-free broadcasting: the best video stream bitrates
When we watch videos on social media or streaming services, we usually do not think about such things as data transfer or what affects video quality besides resolution. This guide defines bitrate as a term and explains its role in video content. Here we also explore how to choose bitrate for videos of different formats and framerates for a buffer-free streaming experience.
What is bitrate: The Full guide
All the computed information is represented in bits of data, which a computer reads as a sequence of zeros and ones. Video files are not excluded in this regard, but unlike other files video files are way bigger in size comparison which makes it important to incorporate such a term as bitrate - the amount of video data to compute per second.
Video bitrate meaning

The importance of bitrate lies in the hardware performance required to read that data as initial and net bandwidth matter. Hardware is required to encode the video information to then interpret it through CPU and GPU into visual value on your screen. The higher the bitrate the more high-end hardware you need to read it. That was significant especially in the 2000s when you could come to an issue that your PC could not flawlessly play some videos.
Video bitrate measurements
We measure bitrate in the same way as you measure your internet speed – in bits per second, but as we mentioned earlier, video files are of a bigger size compared to other files, hence, Megabits per second are in common (Mbps). Do not mess up bits with bytes, because each byte consists of 8 bits. Each second may contain a specific volume of data, which in turn affects the quality of the video.

Each video consists of frames which is the framerate value. Hence, each frame is a standalone image. By sequencing images, we get footage or a video. If an image of 1920 x 1080 resolution size is about 4 MegaBytes, you can count how much 1 second of a 60-fps unencoded video weighs: 60x4= 240 MegaBytes per second. The video editing software compresses the file by removing redundant information and you get a file that is 100-150 times smaller in the output. Eventually, each second of your video is now not 240 MegaBytes but just 8 Megabits. However, 8 Mbps is low quality for 60 fps footage, this is why it is important to encode with optimal video bitrate to find a balance between quality and performance.
How does bitrate affect video quality?

The relation here is straightforward, the higher the bitrate the higher the quality. For instance, to get a good quality video in HD (1080p) format, you need to encode your video with a 6-12K bitrate (6-12 thousand kilobytes or 6-12 Mbps for 30-60 fps videos) on average to get a consistent stream. Otherwise, your screen will tear in pixels of bad quality. To create a video under 4K resolution (3840 x 2160 UHD) you want a bitrate from 35 to 85 Mbps. If you have an old PC build it may struggle to encode UHD (4K) and you get display lag as a result.
Bitrate and bandwidth limits

As we have the bitrate defined as the amount/volume of data to read, you can also consider this number for data transfer. Let’s say we have a 1080p@30fps (1920 x 1080 resolution – FullHD) video of 8 Mbps bitrate, 8 bits = 8 Bytes, this means you require a network capable of transferring at least 1 MegaByte per second to watch this content without stutters or buffering. ISPs usually show their internet speed in exact values as bitrate, so you need an 8 Mbps line (equals to 1 MegaByte download speed per second). Nowadays, Internet Services provide citizens with 100 Mbps lines in common, which means you can watch 4K content without any problems these days. But if your line is like 10 Mbps you are limited to watching full HD content.
How to deal with bandwidth limits

To deal with bandwidth limits, streaming platforms enable buffering features that allow you to pre-download the content to then watch it seamlessly. So basically, you need to spend some time ahead to download the video in advance, and it keeps downloading as you watch in the process. However, if your internet is slow, you can always lower the resolution of a video which in turn lowers the bitrate. In this way, you sacrifice quality for the sake of performance. If you don’t do so, then you get into a buffering issue, as the video goes faster than your internet speed may afford.
Buffer-free broadcasting: the best video stream bitrates
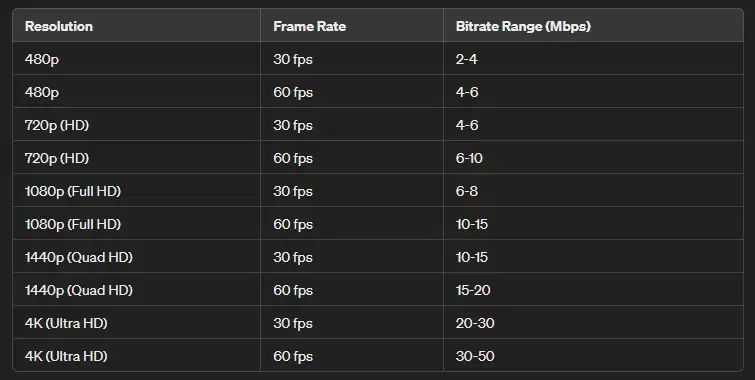
If you want to stay buffer-free, make sure to set video resolution in accordance to balance the desired quality with the performance of your ISP. Here is a table of resolutions with framerate to find the best bitrate for video encoding:
Nowadays we watch content in 1080p 60 fps the most, so you need to make sure to have a bandwidth of at least 15-20 Mbps to avoid buffering. If you want to watch 4K content at a max bitrate of 50-85 Mbps, make sure your ISP corresponds.

Author
Editor with 15 years of experience and enthusiasm about the digital video industry. Managed video editing processes for projects with billions of views and created flagship video products from idea to successful launch. He reads over 40 books a year and travels extensively.





































































